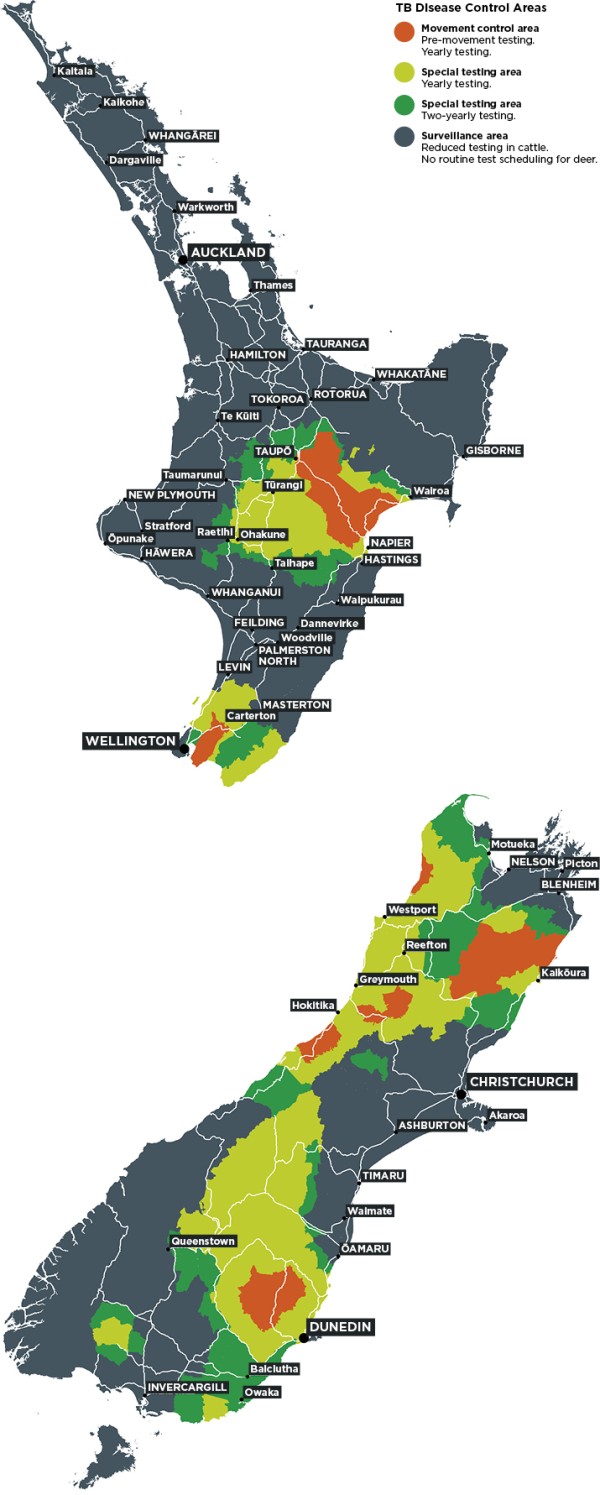
Movement Control Area (MCA)
In MCAs, all cattle or deer on a farm are tested annually. Cattle over 3 months and deer over 8 months of age must have a TB test before they move within an MCA. You must complete the movement within 60 days of the pre-movement test. Stock going direct to slaughter don't require a pre-movement test.
Moving animals from a Movement Control Area (MCA)
Special Testing Area — Annual
In these areas, cattle over 12 months and deer over 15 months of age are tested annually.
Special Testing Area — Biennial
In these areas, cattle and deer over 24 months of age are tested every 2 years.
Surveillance Area
In surveillance areas, cattle over 24 months of age are tested every 5 years.